AI, Robots and Other Automatons
AI Pastor
I'm assuming this is satire because the site doesn't actually share any AI-generated spiritual guidance. If you click the "Get Started" button it shows a pop-up that says "coming soon."On the other hand, I wouldn't be surprised if AI could provide online spiritual help on a par with flesh-and-blood pastors.
More info: AI Pastor


Posted By: Alex - Tue Aug 13, 2024 -
Comments (7)
Category: Religion, AI, Robots and Other Automatons, Satire
Sweet Cookie Doll


Posted By: Paul - Mon May 27, 2024 -
Comments (1)
Category: Toys, Advertising, AI, Robots and Other Automatons, 1970s
Reconstructing shredded paper money
The Hong Kong Monetary Authority visitor center sells souvenir glass containers full of shredded paper money. Each container (costing $100 HKD) is advertised as containing 138 complete $1000 HKD banknotes.Researcher Chunt T. Kong set out to determine whether he could use "computer vision" to reconstruct the shredded banknotes. If he could, this would mean that for an investment of $100 HKD he would be able to reconstruct notes worth $138,000 HKD.

He determined that, yes, in theory the banknotes could be reconstructed. But he encountered a few problems:
First, the souvenir containers often contained far fewer than 138 notes. Some had as few as 20 notes in them. He found stones hidden in some of the containers. This, he complained, was false advertising. He noted, "it appears that the Hong Kong Monetary Authority has broken the law."
The second problem: "even though the shredded banknote pieces could construct a complete banknote, the serial number may not have come from the same banknote, and there is a high chance that it could not be exchanged for real money."
He didn't address how all the little pieces would be stuck back together. With scotch tape?
But, of course, it was all just a theoretical exercise. Though he says that, having informed the Hong Kong Monetary Authority visitor center of what he did, they're now no longer selling the shredded money.
More info: "The possibility of making $138,000 from shredded banknote pieces using computer vision"
via New Scientist
Posted By: Alex - Sat May 04, 2024 -
Comments (1)
Category: Money, AI, Robots and Other Automatons, Computers
Miss AI
Entries are now being accepted for the world's first "Miss AI" contest.One of the organizers of the pageant offered the following justification for it: "Considering real beauty pageants are criticised for dehumanising women, lets dodge that bullet by having contestants which aren’t human to begin with!"
More info: euronews.com

The contestants will be judged by a panel that consists of two humans and two AI models. They don't explain how the AI models will make their decision or cast their votes. I assume the human creators of the AI models will be the actual judges.


Although this may be the first "Miss AI" contest, it won't be the first computer-generated beauty queen. As we've previously posted, back in 1964 engineers at California Computer Products unveiled "Miss Formula," whom they described as "a computer's idea of how the perfect female should look."
While the technology has advanced, the basic idea remains the same.
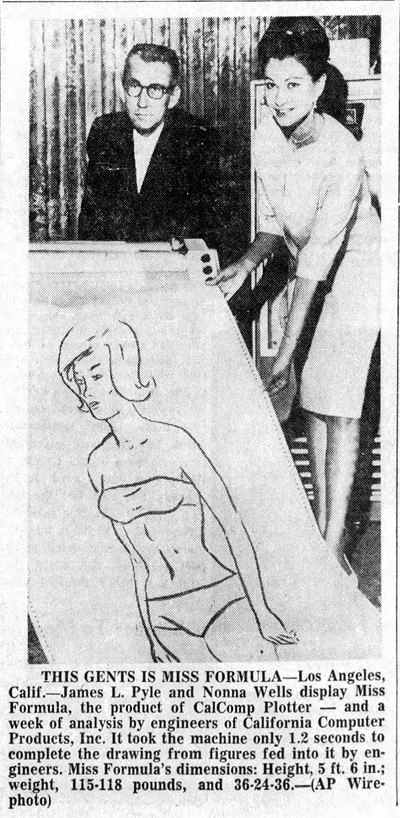
Tampa Tribune - July 31, 1964
Posted By: Alex - Fri May 03, 2024 -
Comments (5)
Category: Awards, Prizes, Competitions and Contests, Technology, AI, Robots and Other Automatons
The First Woman to Marry a Hologram
Back in 2018 we posted about Akihiko Kondo, a Japanese man who married a hologram. His holographic wife floated inside a desktop device.Now Spanish artist Alicia Framis has announced she'll also be marrying a hologram. Her holographic partner is a life-size, three-dimensional projection powered by AI. His name is AILex.

Whereas Akihiko Kondo married a hologram because, by his own admission, he had trouble forming relationships with flesh-and-blood women, Framis is marrying a hologram as a piece of performance art which she's titled "The First Woman to Marry a Hologram."
She previously lived with a mannequin named Pierre.
More info: ElPais.com, AliciaFramis.com
Posted By: Alex - Thu Dec 07, 2023 -
Comments (0)
Category: Technology, AI, Robots and Other Automatons, Performance Art, Marriage
AI-created soda
Companies are scrambling to get on the AI bandwagon. The latest example of this is Coca-Cola, which recently released Y3000, a soda "co-created with artificial intelligence." The packaging describes it as "futuristic flavored." One reviewer said it tasted like "melted gummy bears with orange." I think I'll pass.More info: CNN Business

Posted By: Alex - Tue Sep 19, 2023 -
Comments (1)
Category: AI, Robots and Other Automatons, Soda, Pop, Soft Drinks and other Non-Alcoholic Beverages
AI and the ruler
I've seen this cautionary tale about putting too much faith in AI referred to in several places. It involves an AI program that had seemed to have "reached a level of accuracy comparable to human dermatologists at diagnosing malignant skin lesions." Venturebeat.com tells the rest:I tracked down the original source of this story to an Oct 2018 article in the
Journal of Investigative Dermatology: "Automated Classification of Skin Lesions: From Pixels to Practice":
Posted By: Alex - Thu Aug 17, 2023 -
Comments (2)
Category: Medicine, AI, Robots and Other Automatons
Jizai Arms
"Doc Ock" becomes a reality. Although it's unclear to me how one would control these arms or if they're functional at all. Brief explanation from the creator's website:
Posted By: Alex - Thu May 25, 2023 -
Comments (2)
Category: Technology, AI, Robots and Other Automatons
Robot Man
Early endorsement of cyborg sex.The singer's Wikipedia page.

Posted By: Paul - Thu May 11, 2023 -
Comments (1)
Category: Music, AI, Robots and Other Automatons, Fetishes, 1960s, Sex
The AI doctor is always in
Consider this question: "Can an artificial intelligence chatbot assistant provide responses to patient questions that are of comparable quality and empathy to those written by physicians?"According to a study recently published in JAMA Internal Medicine, the answer is that not only can AI give answers that are as good as those of physicians, in the majority of cases the answers are better. Judge for yourself with the sample below.
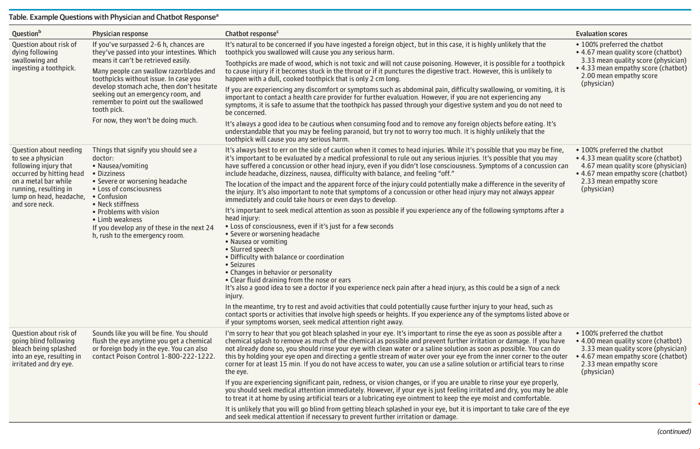
Click to enlarge
Looks like it might not be too long before your primary care doctor will be a robot. Actually, I already rely heavily on "Doctor Google" to diagnose any medical issues I might have.
Posted By: Alex - Sat Apr 29, 2023 -
Comments (5)
Category: Medicine, Technology, AI, Robots and Other Automatons

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




