Health
Bowel evisceration after sneezing
We've previously drawn attention to some of the dangers of coughing and sneezing. Such as the cases of people who sneezed so hard that their eye fell out. Or the woman who coughed out her lung.Now the American Journal of Medical Case Reports has published a case of "bowel evisceration after sneezing." A man sneezed violently while dining at a restaurant and then realized that his intestines had come out of a surgical incision in his stomach. He thought the incision was fully healed. From the journal:
During breakfast, the man sneezed forcefully, followed by coughing. He immediately noticed a “wet” sensation and pain in his lower abdomen. Looking down, he observed several loops of pink bowel protruding from his recent surgical site. He later related that he was unsure of how to proceed, so he covered the exposed intestines with his shirt. He initially decided to drive himself to the hospital, but concerned that changing his position might injure his bowel, his wife requested an ambulance.
To be fair, sometimes sneezing can cause miraculous recoveries, such as the case of the woman whose deafness was cured by a sneeze.
Posted By: Alex - Sun Jun 30, 2024 -
Comments (0)
Category: Health, Surgery
Rancher Glen, the Christmas Seal Cowboy
I'm a little late with this seasonal entry, but I still hope all WU-vies can follow Rancher Glen's advice for a healthy 2024.

Posted By: Paul - Sun Jan 07, 2024 -
Comments (1)
Category: Health, PSA’s, Corporate Mascots, Icons and Spokesbeings, Children, Wild West and US Frontier, Twentieth Century
Hand Waving and Heart Disease
Back in 1997, Dr. Alan N. Rennie reported in the British Medical Journal a correlation between arm movement and heart disease. People who moved their hands and arms around a lot while talking seemed more prone to heart disease. Rennie offered this possible explanation:Good to know that my lazy lack of movement actually has a health benefit.

Chicago Tribune - Jan 10, 1997
Posted By: Alex - Sun Dec 03, 2023 -
Comments (1)
Category: Health, Disease
Pin-Worms may be a family affair
"Fidgeting, nose-picking and a tormenting rectal itch are often tell-tale signs of Pin-Worms . . . Entire families may be victims and not know it."I'm imagining the families who thought the tormenting rectal itches were nothing out-of-the-ordinary.

Super Science Stories - March 1950
Posted By: Alex - Thu Sep 28, 2023 -
Comments (0)
Category: Health, Disease, Advertising, 1950s
Calories Don’t Count
Dr. Herman Taller was arguably ahead of his time with his assertion that a high-protein diet was more effective for weight loss than simply restricting calories. However, it was his promotion of "CDC" (Calories Don't Count) capsules that got him into trouble. He claimed that these capsules not only would help with weight loss but would also lower cholesterol, treat heartburn, improve the complexion, increase resistance to colds, and boost the sex drive. The FDA disagreed, noting that the capsules primarily contained safflower oil. Taller was eventually convicted of mail fraud.More info: Wikipedia, Quackwatch

Posted By: Alex - Sun May 28, 2023 -
Comments (0)
Category: Health, Dieting and Weight Loss
Mysterious Hiccups Cure
Sep 1949: After Robert Meier had suffered from hiccups for 8 days, a mysterious stranger showed up at his house unannounced, draped a wet noodle over Meier's head, and cured his hiccups.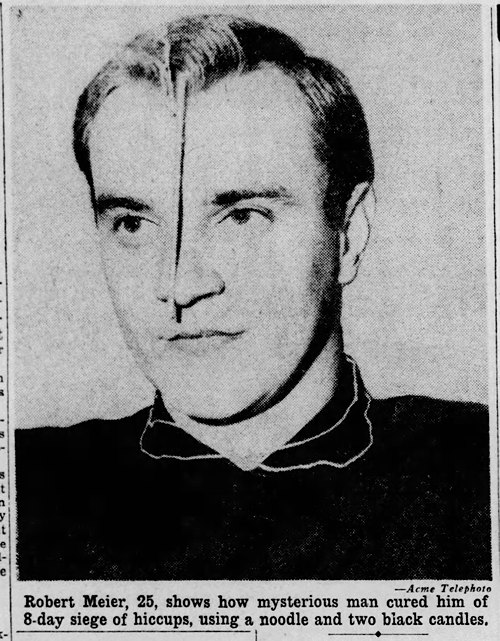

Rochester Democrat and Chronicle - Sep 9, 1949
Posted By: Alex - Sat May 27, 2023 -
Comments (2)
Category: Health, 1940s
The Influence of Sewing Machines on the Health and Morality of Workwomen
Nineteenth-century doctors worried that because sewing machines "produced such an excessive excitement of the sexual organs" they might have an immoral effect upon working women. Text from The Boston Medical and Surgical Journal (Aug 23, 1866):A young woman, whom he had known as the very picture of vigorous health, presented herself at his office in such a condition of emaciation, and with such a change of countenance, that he was greatly shocked at her appearance. The explanation which she gave was as follows.
For seven months, from morning till night, she had worked at a sewing machine, known as the "American machine." The constant motion of the lower extremities in propelling it had produced such an excessive excitement of the sexual organs that she was often compelled to suspend her work; and to the frequency of this effect and the fatigue resulting from it, she attributed the leucorrhoea and attendant loss of flesh and strength from which she was suffering.
The effect seemed to be naturally enough explained by the cause alleged, especially as in some of the machines at which she had worked the pedals were depressed alternately with one food and the other. This case, so serious in its nature, was regarded by M. Guibout as probably the result of a peculiar susceptibility on the part of the patient, and so very exceptional at the time as only worthy of record as a curiosity. But during the past year, he goes on to say, he found in the hospital Saint-Louis, three similar cases; and during the present year he had already found five in the same hospital.
He also adds that within a month "two females, entirely unknown to each other, and working in different shops, called upon him on the same day, to consult him for similar symptoms. The first of these, a blonde, in the most vigorous health when she began to work at the machine, in seven or eight months has become enfeebled, her embonpoint was gone, her general health had declined, and she had become the subject of a profuse leucorrhoea, which was daily increasing.
She said also that many of the girls in the same establishment were affected in the same way, by the same cause, "the continual movement of the lower limbs, the jar and the swaying of the body." She denied, however, that she had been troubled by the special symptoms mentioned by the first patient, but said that many of her companions had been. Many of them had been so annoyed as to be obliged frequently to suspend their work and leave the shop for the purpose of bathing with cold water.
The second of these two patients was a brunette, of entirely different temperament from the other. She had been obliged to give up her place after working at the machine for a year, on account of the same symptoms. To the inquiry as to any local excitement produced by it, she answered in the affirmative. To translate her own words: "Among 500 women who worked with me, there were at least 200 who, to my knowledge, suffered as I did; so that the operatives were constantly changing, none of them being able to stay long. It is a constant going and coming of women, who enter strong and well, and who go out weak and emaciated."
M. Guibout went on to recite other instances equally serious, but it is not necessary to quote them. The subject is one of very grave moment and worthy of the consideration of every physician. In the discussion which followed the reading of his paper, some of the members of the Society were disposed to question the frequency of the peculiar symptoms which he reported. He, however, maintained his position, urging that it was very difficult to get a confession from many of the victims of the machine, so that when directly interrogated, a negative response should not always be received as the truth. The large number of cases which had come under his own observation had led him to lay this painful subject before the Society.
I asked Microsoft's AI image creator to produce an image based on the article's title, and this is what it came up with:

Posted By: Alex - Wed May 17, 2023 -
Comments (6)
Category: Health, Medicine, Nineteenth Century
Mechanical Chiropractor
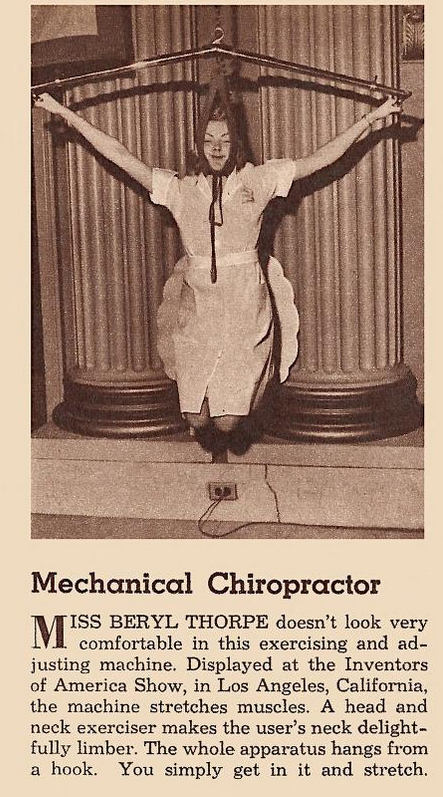
Source.
Posted By: Paul - Sun Apr 30, 2023 -
Comments (0)
Category: Health, Hobbies and DIY, Lawsuits, 1940s
Burned by a belch
In 1890, Dr. James McNaught of Manchester reported in The British Medical Journal the strange case of a 24-year-old factory worker whose burp caught on fire while he was holding a match, badly burning his face and lips. McNaught managed to replicate the burning belch with the man in his office, confirming it really did happen. He diagnosed the problem as the "eructation of inflammable gas" from the man's stomach.McNaught concluded that the man suffered from a disorder that caused food to ferment in his stomach and produce flammable gas, instead of being digested. He advised the man to eat foods that would pass more quickly out of his stomach, to avoid the fermentation.
More info: British Medical Journal, "A Case of Dilatation of the Stomach Accompanied by the Eructation of Inflammable Gas"

Posted By: Alex - Fri Apr 21, 2023 -
Comments (3)
Category: Health, Stomach, Smells and Odors
Follies of the Madmen #560
Posted By: Paul - Wed Mar 29, 2023 -
Comments (1)
Category: Anthropomorphism, Body, Cryptozoology, Health, Advertising, 1960s, 1970s

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




