Literature
Shakespeare’s Greatest Hits
The Bard's words as you have never dared to imagine them before.
Posted By: Paul - Thu Jan 05, 2023 -
Comments (2)
Category: Literature, Music, Vinyl Albums and Other Media Recordings, 1960s
foew&ombwhnw
foew&ombwhnw, by Dick Higgins, was published in 1969 by Something Else Press. The title was an acronym for "freaked-out electronic wizards & other marvellous bartenders who have no wings."The design of the book was unusual. It was made to look like a prayer book, with black cover and thin pages. Inside, the text was divided into four columns. To read the book in order you had to first read all the left-hand columns, then all the second-to-left columns, etc.
The book itself was a collection of essays, plays, and poems. Or, as Higgins described it, "a grammar of the mind and a phenomenology of love and a science of the arts as seen by a stalker of the wild mushroom."
Copies of it generally go for over $100, for anyone interested in adding it to their collection of weird books.
More info: DickHiggins.org
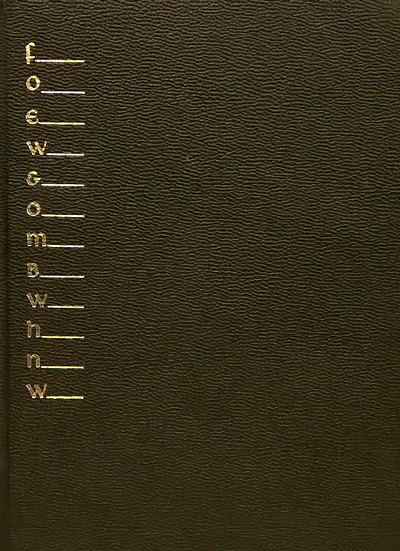

source: printedmatter.org
Posted By: Alex - Sat Dec 10, 2022 -
Comments (0)
Category: Literature, Books, 1960s
Moby Dick, from the whale’s perspective
Artist Wu Tsang's six-hour looping film Of Whales, displayed recently at the 59th Venice Biennale, reimagines the story of Moby Dick, from the whale's perspective. Details from artnet.com:"The work is about reflection in both senses, as well as capturing the whale come out of the water and dive back into it," the artist said, looking at the looping underwater scenes in which the whale remains unseen but is hinted at in fluctuating camera movements. Images of jellyfish float through the water and spiral beams of light reflect across forceful waves.
It doesn't sound like Ahab and crew ever make an appearance, which seems to me like a bit of a lost opportunity. It could have been six hours of jellyfish and waves, followed by five minutes of crazed sailors.
Posted By: Alex - Thu May 05, 2022 -
Comments (0)
Category: Literature, Movies
A History of Mechanical Horses
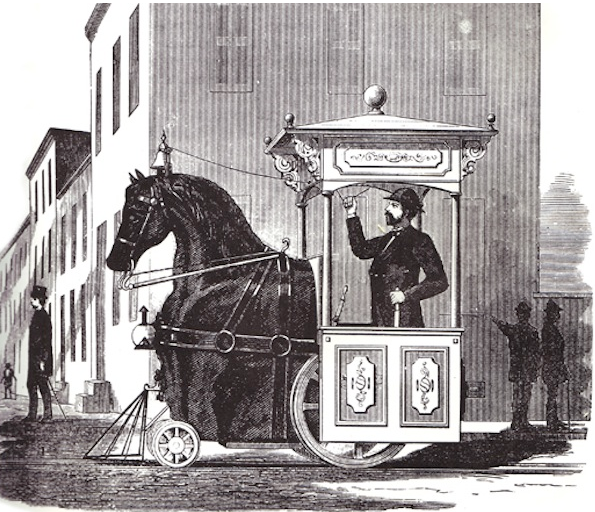
Read the piece here.
There should be a separate article on mechanical horses in literature. My favorite one occurs in these two novels by Roger Zelazny.


Posted By: Paul - Tue Nov 30, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Animals, Inventions, Literature, Fantasy, AI, Robots and Other Automatons, Nineteenth Century, Twentieth Century
The Odd Downfall of Mary Carolyn Davies
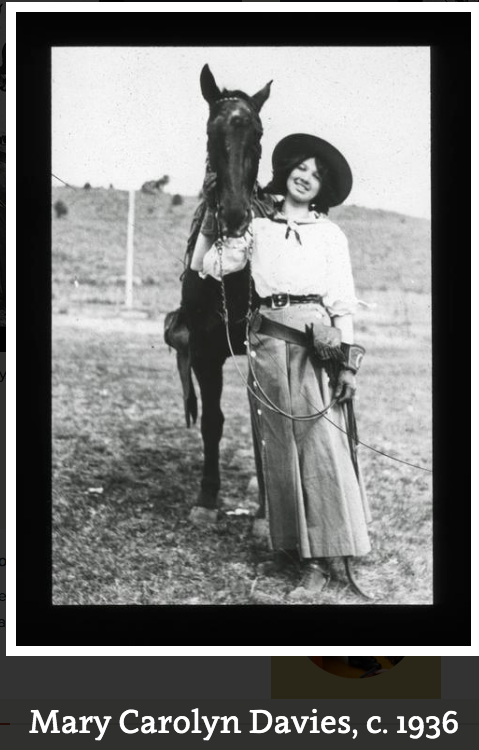

From pulp writer and poet to Skid Row: writing has never been an easy career.
Read the whole arc of her life here.
Read some of her fiction at the Internet Archive.
Newspaper clip from The News Journal (Wilmington, Delaware) 08 Feb 1940, Thu Page 20




Posted By: Paul - Sun Aug 29, 2021 -
Comments (0)
Category: Eccentrics, Literature, Money, Twentieth Century
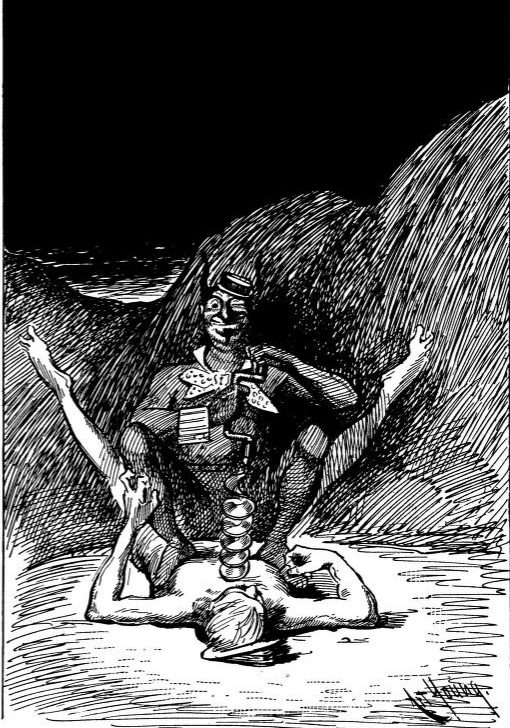
Hell Up To Date
A modern (1894) version of THE INFERNO. Many more weird illustrations at the link, where you may read the whole thing.

Posted By: Paul - Sun Aug 22, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Fate, Predetermination and Inevitability, Literature, Religion, Parody, Satire, Nineteenth Century
The Error in The Ambassadors
The first American edition of Henry James's novel The Ambassadors was published in 1903. But it took 47 years before anyone noticed that there seemed to be a glaring error in it, and the person who noticed was a Stanford undergrad, Robert E. Young. As told by Frances Wilson in the Times Literary Supplement:this reversal of chapters was missed by James, not once but twice. He missed it when he checked the proofs of the novel set by Harper and he missed it again in 1908, during his scrupulous revision of The Ambassadors for Scribner’s New York Edition of his work.
The chapters had actually been printed in the correct order in a British edition, published before the American one. But every subsequent American (and British) edition had used the incorrect order, until Young pointed out the mistake.

Young blamed James's writing style for the error. He concluded his 1950 article in the journal American Literature (in which he exposed the error) with this paragraph:
Naturally, this charge riled James's fans, some of whom sought to defend him. Most notably, in 1992 scholar Jerome McGann argued that James might have intended for the chapters to be in that order. From Wikipedia:
It doesn't seem that many people buy McGann's argument, so the consensus remains that the chapters were out of order and James never noticed.
Posted By: Alex - Mon Mar 22, 2021 -
Comments (1)
Category: Literature, Goofs and Screw-ups
Avakoum Zahov, the Soviet James Bond
Avakoum Zahov was a fictional secret agent who featured in the novels of the Bulgarian writer Andrei Gulyashki. Zahov made his first appearance in the 1959 novel The Zakhov Mission. He returned in the 1966 novel Avakoum Zahov versus 07 — in which he battles and defeats a British agent known as '07'.
image source: pulp curry
There have been persistent rumors that Gulyashki created Zahov at the behest of the KGB in an attempt to produce a Soviet James Bond. Details from an article by Andrew Nette:
It is not clear where McCormick got his information, but others have since picked up the claim and run with it. The Penguin Dictionary of Literary Terms and Literary Theory states that Gulyashki ‘was invited by the KGB to refurbish the image of Soviet espionage which had been tarnished by the success of James Bond’. Likewise, Wesley Britton claims in Beyond Bond: Spies in Fiction and Film that, in 1966, the Bulgarian novelist was hired by the Soviet press to create a communist agent to stand against the British spy ‘because of Russian fears that 007 was in fact an effective propaganda tool for the West’.
"My name is Zahov, Avakoum Zahov" just doesn't have the same ring as "Bond, James Bond".
Posted By: Alex - Sat Feb 06, 2021 -
Comments (4)
Category: Literature, Books, Spies and Intelligence Services, 1960s
TLALAATALA
Jose Luis Castillejo (1930-2014) described himself as a "modern writer". In 1969 he self-published The Book of I's, which was a book that consisted entirely of the letter 'i', printed repeatedly on several hundred pages. He said that he wrote it to "end the torrent of words we call literature." It's read below by Fernando Millan. (He begins reading the book shortly after the 1-minute mark).In 2001, Castillejo explored the letters T, L, and A, with his release of TLALAATALA. It's read again by Millan.
As you might guess, writing wasn't Castillejo's day job. He earned his living as a diplomat, serving as General Consul of Spain in Stuttgart, as well as Spanish ambassador to Nigeria and Benin.
More info about Castillejo: caac.es
Posted By: Alex - Fri Dec 11, 2020 -
Comments (3)
Category: Literature, Books
The Quest For A Blonde Mistress
Publisher Emanuel Haldeman-Julius debuted his "little blue books" in 1919. These were cheaply bound, pocket-sized literary and academic works designed to make highbrow culture accessible to the masses. They sold for five cents each.Haldeman-Julius didn't do this for charity. He wanted to sell as many titles as possible, and to achieve this he would often alter the titles to make them more appealing to consumers. Basically, he would sex up the titles.
For example, he added the subtitle "The Quest for a Blonde Mistress" to Theophier Gautier’s novel The Fleece of Gold. Sales leapt from 6000 to 50,000 copies a year. (Apparently, 'quest for a blonde mistress' is an accurate description of the book's plot.)

Other titles that benefitted from a title change:
• "The Tallow Ball" by Guy de Maupassant became "A French Prostitute's Sacrifice."
• None Beneath the King by José Zorrilla became None Beneath the King Shall Enjoy This Woman.
• Victor Hugo’s The King Amuses Himself became The Lustful King Enjoys Himself.
Haldeman-Julius didn't always make the titles more risque. Sometimes he emphasized self-improvement, and that also had a positive effect on sales. For example, sales of Thomas De Quincey’s Essay on Conversation jumped when it was renamed How To Improve Your Conversation. Similarly, Arthur Schopenhauer’s Art of Controversy became How to Argue Logically. And Dante and Other Waning Classics became Facts You Should Know About the Classics.
Haldeman-Julius was totally open, even boastful, about this strategy. From his book The First Hundred Million:
Posted By: Alex - Tue Jul 07, 2020 -
Comments (3)
Category: Literature, Books

| Who We Are |
|---|
| Alex Boese Alex is the creator and curator of the Museum of Hoaxes. He's also the author of various weird, non-fiction, science-themed books such as Elephants on Acid and Psychedelic Apes. Paul Di Filippo Paul has been paid to put weird ideas into fictional form for over thirty years, in his career as a noted science fiction writer. He has recently begun blogging on many curious topics with three fellow writers at The Inferior 4+1. Contact Us |




